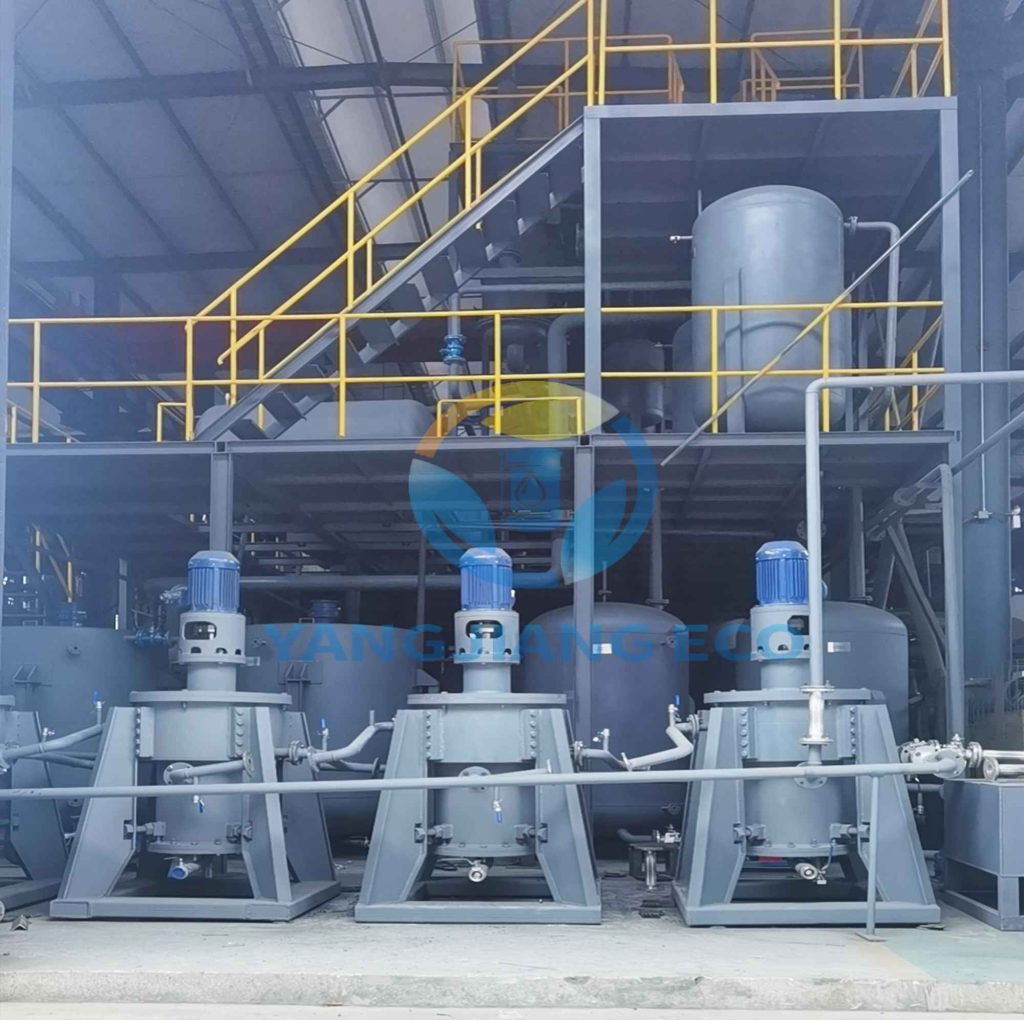
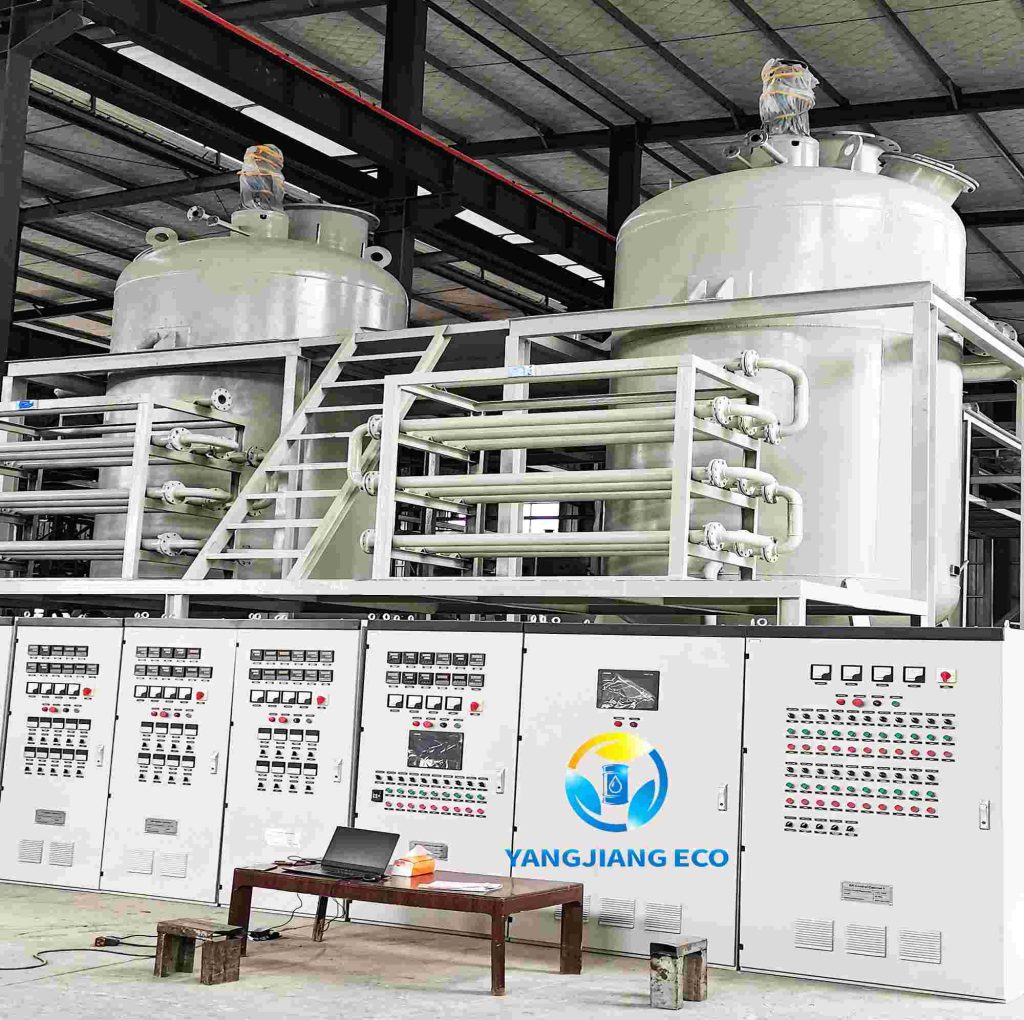
When it comes to extracting oil from oil-bearing materials, two main technologies dominate the industry: solvent extraction and mechanical extraction. Both techniques have distinct processes, advantages, and limits. Understanding the distinctions between these approaches is critical for businesses and manufacturers seeking the most efficient and cost-effective approach to oil recovery. In this post, we’ll look at what oil solvent extraction and mechanical extraction are, how they work, the fundamental distinctions, the benefits and drawbacks, and which approach is ideal for you.
What is Oil Solvent Extraction?
Oil solvent extraction is a chemical process for extracting oil from source materials. This technique is commonly employed when producing edible oils, biodiesel and industrial lubricants; typically using solvents like hexane or ethanol to aid in breaking down materials containing oil-containing molecules more effectively than mechanical means; the method especially useful when working with feedstocks that contain large concentrations of cellular structures that contain oil content.
Oil Solvent Extraction Process
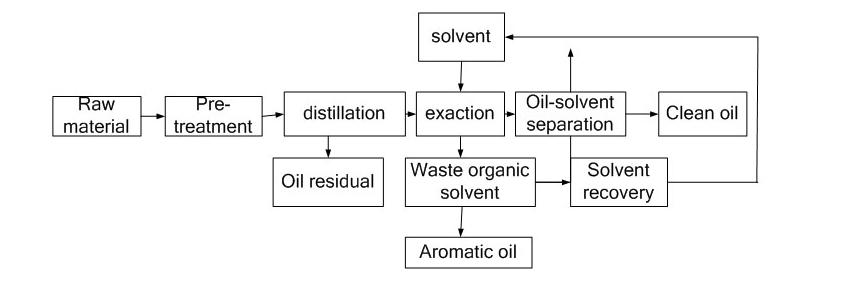
The process of extraction of oil solvents is a very efficient technique to extract oil from oil-bearing substances in particular those with a very little oil content. This is a step-by-step guide to the process:
- Preparation: The material that contains oil like nuts or seeds, is first cleansed to get rid of impurities and then dried to lower the moisture content. Then, it is crushed or flaked to increase the surface area which allows better contact with solvent.
- Extraction: The material is pumped into an extractor where it is brought into contact of a liquid. Typically, it’s Hexane. This solvent dissolves the oil, resulting in the miscella (oil-solvent mix). The solid residue, also known as meal remains in the sand.
- Separation: Miscella gets separated from the meal solid. After that, the meal gets processed in order to remove any solvent that remains that can be used during the extraction process.
- Distillation: A miscella goes through distillation to extract it from its solvent. The solvent is then recovered and reused, whereas raw oil gets gathered to be further processed.
- Refining: The crude oil undergoes refinement to eliminate impurities such as free fatty acids, colorants and odors, which results in a final product that is suitable for industrial or consumer use.
This technique is extremely efficient in maximizing oil yield, particularly for substances with a low oil content and is used extensively for large-scale production of oil. It requires careful handling of solvents as well as modern technology to guarantee safety as well as effectiveness.

What is Mechanical Extraction?
Mechanical extraction, often called pressing, is a method to extract oils from oil-bearing substances by using force. This technique is extensively used to extract oil from materials with a large amount of oil like coconuts, olives, or sunflower seeds, as well as peanuts. In contrast to solvent extraction which is a chemical process, mechanical extraction doesn’t involve chemical processes, which makes ita more natural and eco-sustainable method. There are two main kinds of mechanical extraction: hot and cold pressing.

- Cold pressing: This technique is the process of extracting oil at low temperatures, usually less than 50 deg C (122 degrees F). Cold pressing retains the oil’s flavor and aroma as well as nutritional qualities, making it ideal for the production of premium edible oils such as olive oils that are extra-virgin, or coconut oil cold-pressed. It is usually used in situations where keeping the purity of the oil and the health benefits it offers is of paramount importance.
- Heating the Press: In this process the oil-bearing material is heated prior to or during the process of pressing. The heating reduces the viscosity of oil, allowing to increase the efficiency of extraction and yield. Hot pressing is often used in industrial oils or in situations where maximizing yield is more crucial than maintaining the oil’s natural characteristics.
Mechanical extraction can be described as a less complicated and more conventional method of extraction in comparison to solvent extraction and is especially suitable for small to medium-sized operations, or to produce oils that are intended for direct consumption without any extensive refinement.

Key Differences Between Oil Solvent Extraction and Mechanical Extraction
When comparing solvent extraction and mechanical extraction, several key factors influence their efficiency, cost, and sustainability. The table below highlights the major differences between these two oil recovery methods:
| Factor | Solvent Extraction | Mechanical Extraction |
| Oil Yield | Increased yield, extracts more oil from the raw materials | Lower yield, but some oils remain in relics |
| Oil Quality | It may require refining to eliminate solvent residues | Natural flavors and nutrients are preserved. |
| Processing Method | Chemical solvents used for dissolving and extracting oil | Utilizes pressure to isolate oil |
| Environmental Impact | This requires careful handling of solvents as well as disposal | Greener and more sustainable with no chemicals to use |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment for specialized equipment | Less expensive setup, easier machine |
| Operational Complexity | More complicated requires solvent recovery as well as refining | Simpler to use, requiring smaller processing steps |
| Suitability for Feedstocks | It is ideal for materials with low oil content. | Ideal for materials with high oil content. |
While solvent extraction maximizes oil recovery, mechanical extraction is a more natural and environmentally benign option. The intended oil quality, processing size, and sustainability goals all influence which method is chosen.
Pros and Cons of Oil Solvent Extraction & Mechanical Extraction
Pros and Cons of Oil Solvent Extraction
One of the main benefits of solvent extraction for oil is the high efficiency of its yield. The method is able to extract an increased amount of oil than mechanical extraction, which makes it especially beneficial for materials that have lower levels of oil. In addition, solvent extraction is extremely adaptable since it can be utilized to a variety of feedstocks like biomass, oilseeds, and even Shale oil. Its ability to scale up makes it a great choice for industrial applications where the highest oil recovery is crucial.
However, the use of chemical solvents can pose some difficulties. This procedure requires the careful handling of chemical substances, like Hexane, which could be dangerous if not handled correctly. This method requires additional refinement steps to remove any solvent residues. This can result in higher operational costs. Furthermore, solvent extraction equipment requires a larger initial investment as well as ongoing maintenance, which makes it less accessible to smaller-scale producers.
Pros and Cons of Mechanical Extraction
Mechanical extraction is renowned because of its capacity to create pure and chemical-free oil. Because this method doesn’t depend on solvents, it is typically used in the food industry in which conserving the natural taste and nutritional qualities of oil is essential. Furthermore, mechanical pressing is easy to use and maintain, which requires less sophisticated machinery as compared to solvent-based processes. Its ecological nature, because of the absence of chemicals, makes it a viable alternative to produce sustainable products.
On the flip side mechanical extraction usually produces lower amounts of oil than solvent extract since some oil remains within this raw substance. This can result in greater requirements for raw materials to achieve production goals. Another issue is that mechanical pressing might not be appropriate for all feedstocks, particularly ones with highly bound oil molecules. In addition, the process could create heat through friction, which can reduce the quality of heat-sensitive oils, affecting their nutritional value as well as longevity.
Which Method is Best for Oil Recovery?

The decision between oil solvent extraction as well as mechanical extraction is based on a variety of factors, including the type of raw material, the preferred oil’s grade, the production size, and environmental concerns.
- High-yield extraction: Solvent extraction may be the preferred option as it can extract virtually all of the available oil from low-oil-content substances.
- For pure organic, chemical-free oil: Extraction by mechanical means is the preferred method particularly for oils that are edible, in which consumers are concerned about pureness and the least amount of processing.
- Large-scale industrial production: Solvent extraction is more efficient because of its higher rate of recovery making it cost-effective in spite of larger initial investments.
- for organic or small-scale extraction: Mechanical extraction is less complicated, and more eco-friendly and in line with the need for pure, unprocessed oils.
There are many industries that combine both methods – using mechanical pressing to first get rid of the majority of oil, then solvent extraction to extract any oil left, and optimizing the efficiency.

To maximize oil recovery using solvent extraction by investing in premium base oil solvent extraction equipment is vital. These machines use sophisticated systems for solvent recovery that ensure efficient extraction with the least amount of environmental impact and loss of solvent. Modern models are engineered to automate and ensure precision control and efficiency in energy use, which makes the ideal choice for large-scale oil recovery. For biodiesel, edible oil production, or industrial use selecting the appropriate solvent extraction equipment can dramatically improve efficiency and profits.
Have any interest in an oil solvent extraction machine? Please feel free to contact YANGJIANG for more information.
Recommended Products