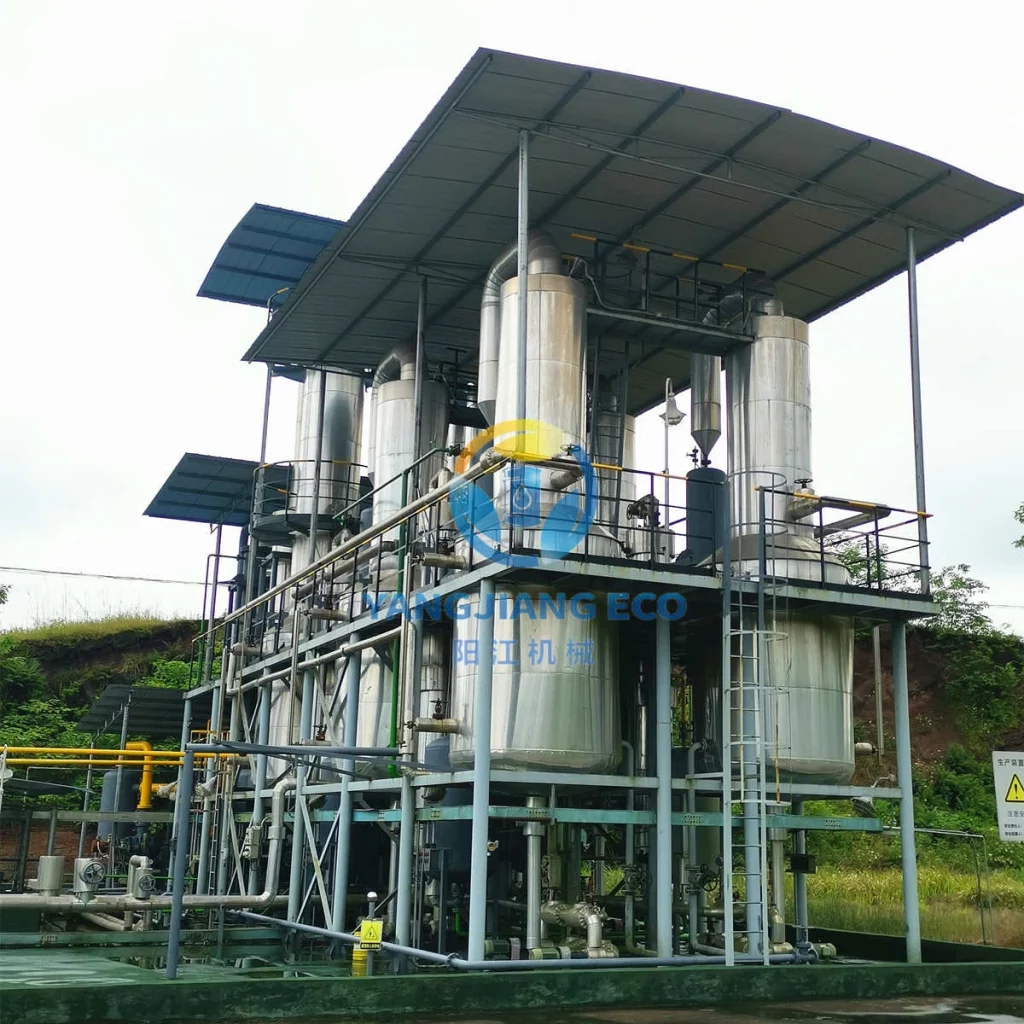
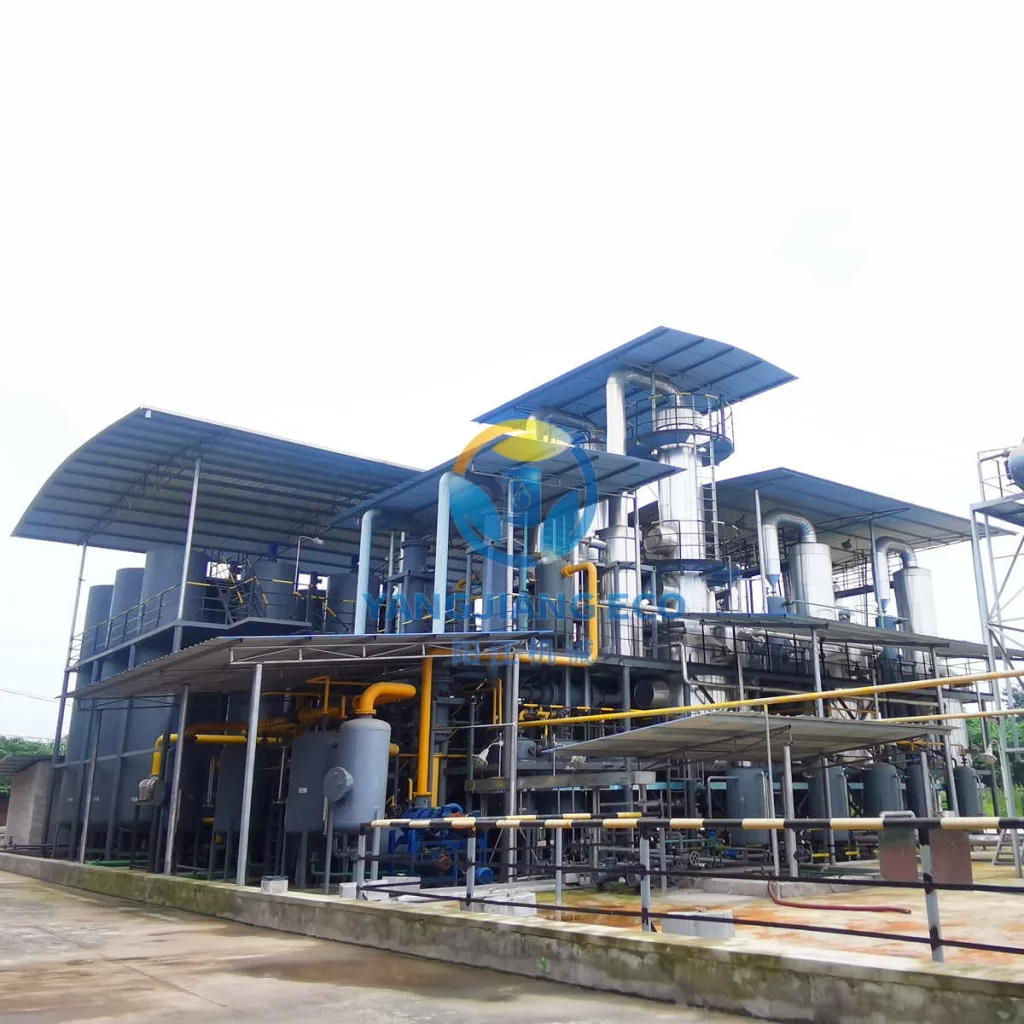
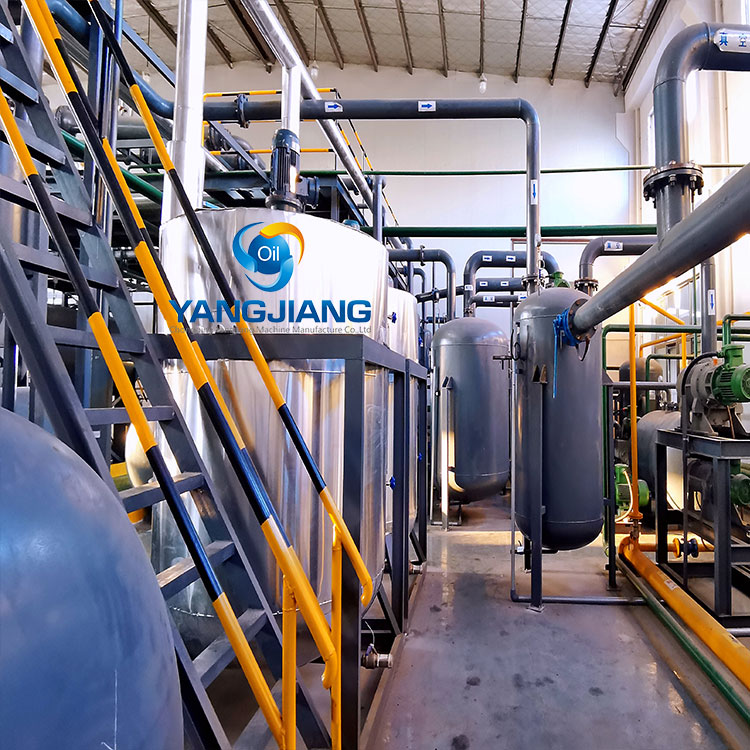
The transportation industry faces growing pressure to reduce its environmental impact and meet global carbon neutrality goals. A key challenge is minimizing harmful emissions from fossil fuels, especially diesel. Sulfur in diesel contributes significantly to air pollution and harms human health and the environment. Diesel desulfurization is vital in addressing these issues and advancing carbon-neutral transportation. In this article, we will examine the environmental and health impacts of sulfur in diesel, the desulfurization process, its benefits, and its role in achieving carbon neutrality in the sector.

Environmental and Health Impacts of Sulfur in Diesel
Sulfur is a naturally occurring element found in crude oil and, consequently, in diesel fuel. When diesel fuel containing sulfur is burned in engines, it produces sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and other sulfur-based compounds, such as sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants have significant environmental and health implications:
1. Air Pollution and Acid Rain
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) plays a significant role in air pollution. Once emitted into the air, it combines with water vapor, oxygen, and other chemicals to produce sulfuric acid, which then contributes to the formation of acid rain. This acid rain harms aquatic habitats, degrades soil health, and damages plant life, ultimately disrupting ecosystems. Moreover, the corrosive nature of acid rain can erode buildings and infrastructure, leading to considerable economic expenses for repairs and upkeep.
2. Climate Change
Although sulfur compounds themselves are not significant greenhouse gases, they can influence climate indirectly. Sulfur dioxide can lead to the formation of aerosols that reflect sunlight, thereby having a cooling effect on the Earth’s atmosphere. However, this “global dimming” effect is short-lived and is outweighed by the long-term negative consequences of diesel emissions on air quality and human health.
3. Health Risks
Sulfur compounds, especially particulate matter (PM), pose significant risks to both respiratory and cardiovascular health. Diesel combustion generates fine particulate matter (PM2.5) that can infiltrate the lungs and enter the bloodstream, causing a range of health problems, including asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, heart disease, and even premature death. Additionally, sulfur emissions play a key role in the formation of ground-level ozone (smog), which further deteriorates air quality and aggravates respiratory conditions.
What is the Diesel Desulfurization Process?
Diesel desulfurization is a refining technique aimed at lowering the sulfur content in diesel fuel. Since sulfur is naturally present in crude oil and consequently in diesel, its combustion releases harmful sulfur compounds into the atmosphere. To minimize these detrimental effects, the desulfurization process eliminates sulfur from the fuel, resulting in a cleaner, more environmentally friendly product.
The primary method of diesel desulfurization is Hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which involves treating diesel fuel with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. Here’s how it works:
- Hydrogen Addition: The diesel fuel is combined with hydrogen gas under high pressure and temperature.
- Catalytic Reaction: The mixture is then passed over a catalyst, typically made from metals like cobalt-molybdenum or nickel-molybdenum. These catalysts facilitate a chemical reaction in which sulfur compounds in the diesel react with hydrogen to form hydrogen sulfide (H₂S).
- Separation: The hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) is then separated from the fuel and removed, leaving behind a diesel product with significantly reduced sulfur content.
This method is highly efficient and can remove up to 95-99% of sulfur, producing Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD), which is required in many countries to meet strict emissions standards.
Alongside hydrodesulfurization (HDS), biodesulfurization is an emerging, environmentally friendly technique that employs microorganisms or enzymes to naturally degrade sulfur compounds. Although it is still under development for widespread industrial application, biodesulfurization presents a potentially more sustainable solution for reducing sulfur in diesel, as it doesn’t require high temperatures or hydrogen.
Together, these methods are essential for producing cleaner diesel fuel, thereby minimizing environmental impact and improving public health.
What are the Benefits of Diesel Desulfurization?

Diesel desulfurization offers several key benefits that extend beyond regulatory compliance, contributing to cleaner air, better engine performance, and long-term environmental sustainability:
- Health Benefits: Reducing sulfur content in diesel fuel minimizes the production of harmful particulate matter (PM) and sulfur-based compounds. This, in turn, lowers the likelihood of respiratory and cardiovascular issues, including asthma and heart attacks, which are associated with exposure to diesel exhaust.
- Improved Air Quality: The removal of sulfur from diesel fuel substantially cuts down sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions, thereby helping to reduce air pollution, smog, and the formation of acid rain. As a result, air quality improves, leading to positive outcomes for both the environment and public health.
- Longer Engine Life: By minimizing sulfur-related damage, desulfurized diesel helps extend the lifespan of engine components. This reduces maintenance requirements and increases the overall durability of diesel-powered vehicles.
- Enhanced Engine Efficiency: Desulfurized diesel fuels lead to better combustion efficiency in engines. With less sulfur, engines operate more smoothly, reducing the formation of engine deposits and improving fuel economy, which translates to lower operational costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent environmental standards for sulfur content, such as the ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) regulations, ensures that companies stay in compliance with environmental laws, avoiding fines and supporting sustainable practices.
Diesel Desulfurization and Carbon Neutrality

Achieving carbon neutrality in the transportation sector is a complex task that requires a multifaceted approach. While reducing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions is central to this goal, addressing the environmental impacts of sulfur in diesel fuel is a crucial first step. Diesel desulfurization can improve fuel quality, supporting cleaner technologies, and then contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
Diesel desulfurization plays a key role in advancing carbon neutrality by improving the performance of modern engines and cutting down on harmful emissions. Eliminating sulfur from diesel fuel helps to decrease the production of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂), particulate matter (PM), and acid rain. This not only benefits air quality and public health but also facilitates the use of cleaner technologies like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, which are effective in lowering nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. These after-treatment solutions are essential for complying with stricter environmental standards and reducing the overall carbon footprint of diesel-powered vehicles.
Moreover, ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) serves as a stepping stone toward cleaner, more sustainable fuel options. By removing sulfur, desulfurized diesel becomes more compatible with alternative fuels like biodiesel, which have a smaller carbon footprint. This compatibility is crucial for seamlessly integrating biofuels into current infrastructure, facilitating a smooth shift to low-carbon fuel systems.

Furthermore, the process of diesel desulfurization helps maximize the efficiency of hybrid and electric vehicles that rely on diesel as a backup fuel. As fuel efficiency improves and emissions are reduced, the path toward a carbon-neutral transportation sector becomes increasingly feasible.
In a word, while desulfurization itself does not eliminate CO₂ emissions, it is integral to enabling the cleaner technologies and fuels necessary for achieving carbon neutrality.
Use of Diesel Desulfurization Machines
Diesel desulfurization relies on advanced machinery to efficiently remove sulfur from diesel fuel, ensuring compliance with environmental standards. Key equipment in this process includes hydrodesulfurization reactors, catalysts, hydrogen supply systems, and sulfur recovery units. These machines work in concert to remove sulfur compounds and convert them into less harmful substances, improving fuel quality and engine performance.

YANGJIANG, a leading manufacturer of diesel desulfurization equipment, provides high-quality solutions for refining and fuel treatment. Specializing in oil recycling and refining technologies, YANGJIANG offers state-of-the-art desulfurization machines designed to optimize fuel purity and reduce emissions. Our hydrogenation reactors and sulfur recovery systems ensure efficient sulfur removal, contributing to the production of ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD). By using YANGJIANG’s advanced systems, refineries can improve fuel efficiency, extend engine life, and meet stringent environmental regulations, supporting a cleaner and more sustainable transportation industry.
For more information, visit YANGJIANG Oil Recycling Plant.
Recommended Products





